Methamphetamine
Methamphetamine[note 1] (contracted from N-methylamphetamine) is a potent central nervous system (CNS) stimulantthat is mainly used as a recreational drugand less commonly as a second-line treatment for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and obesity.[17]Methamphetamine was discovered in 1893 and exists as two enantiomers: levo-methamphetamine and dextro-methamphetamine.[note 2]Methamphetamine properly refers to a specific chemical, the racemic free base, which is an equal mixture of levomethamphetamine and dextromethamphetamine in their pure amine forms. It is rarely prescribed over concerns involving human neurotoxicityand potential for recreational use as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant, among other concerns, as well as the availability of safer substitute drugs with comparable treatment efficacy. Dextromethamphetamine is a much stronger CNS stimulant than levomethamphetamine.
Both methamphetamine and dextromethamphetamine are illicitly trafficked and sold owing to their potential for recreational use. The highest prevalence of illegal methamphetamine use occurs in parts of Asia, Oceania, and in the United States, where racemic methamphetamine, levomethamphetamine, and dextromethamphetamine are classified as schedule II controlled substances. Levomethamphetamine is available as an over-the-counter (OTC) drug for use as an inhaled nasal decongestant in the United States.[note 3] Internationally, the production, distribution, sale, and possession of methamphetamine is restricted or banned in many countries, due to its placement in schedule II of the United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances treaty. While dextromethamphetamine is a more potent drug, racemic methamphetamine is sometimes illicitly produced due to the relative ease of synthesis and limited availability of chemical precursors.
In low to moderate doses, methamphetamine can elevate mood, increase alertness, concentration and energy in fatigued individuals, reduce appetite, and promote weight loss. At relatively high doses, it can induce psychosis, breakdown of skeletal muscle, seizures and bleeding in the brain. Chronic high-dose use can precipitate unpredictable and rapid mood swings, stimulant psychosis (e.g., paranoia, hallucinations, delirium, and delusions) and violent behavior. Recreationally, methamphetamine's ability to increase energy has been reported to lift mood and increase sexual desire to such an extent that users are able to engage in sexual activity continuously for several days.[20]Methamphetamine is known to possess a high addiction liability (i.e., a high likelihood that long-term or high dose use will lead to compulsive drug use) and high dependence liability (i.e. a high likelihood that withdrawal symptoms will occur when methamphetamine use ceases). Heavy recreational use of methamphetamine may lead to a post-acute-withdrawal syndrome, which can persist for months beyond the typical withdrawal period. Unlike amphetamine, methamphetamine is neurotoxic to human midbrain dopaminergic neurons.[21] It has also been shown to damage serotoninneurons in the CNS.[22][23] This damage includes adverse changes in brain structure and function, such as reductions in grey matter volume in several brain regions and adverse changes in markers of metabolic integrity.[23]
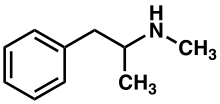
Methamphetamine belongs to the substituted phenethylamine and substituted amphetamine chemical classes. It is related to the other dimethylphenethylamines as a positional isomer of these compounds, which share the common chemical formula: C10H15N1.

No comments:
Post a Comment